The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that has been gaining popularity, especially among students dealing with concentration challenges. For students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), this technique can be particularly beneficial. It promotes focused work sessions followed by short breaks, which helps to mitigate distractions and enhance focus. In this article, we will explore the nuances of ADHD, the Pomodoro Technique, and how these two can work together to improve concentration in students.
Understanding ADHD and Its Impact on Concentration
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. Those with ADHD often struggle with various symptoms, including impulsivity, hyperactivity, and most pertinently, difficulties in sustaining attention. This lack of focus can greatly impact academic performance and personal productivity.
Defining ADHD
ADHD is characterized by patterns of behavior that include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, from difficulty organizing tasks to challenges in sitting still during lectures. According to the American Psychiatric Association, these symptoms can lead to significant impairment in social, academic, and occupational settings, necessitating effective management strategies. The disorder is often diagnosed in childhood, but many individuals carry the symptoms into adulthood, affecting their professional lives and relationships. Early diagnosis and intervention can be pivotal in helping individuals manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
The Relationship Between ADHD and Concentration
Students with ADHD often find it challenging to maintain concentration during tasks that require sustained focus, such as reading or prolonged studying. This difficulty can lead to unfinished assignments, decreased academic performance, and frustration for both students and educators. Understanding this relationship is crucial for developing effective interventions, including methods like the Pomodoro Technique. This technique encourages short bursts of focused work followed by brief breaks, which can help individuals with ADHD manage their attention spans more effectively. Additionally, incorporating engaging and interactive teaching methods can also enhance concentration by catering to the diverse learning styles of students with ADHD.
Moreover, environmental factors play a significant role in concentration levels for those with ADHD. A cluttered or noisy workspace can exacerbate difficulties in focusing, making it essential to create a conducive learning environment. Strategies such as minimizing distractions, using organizational tools, and establishing a routine can greatly benefit individuals with ADHD. Furthermore, support from educators, family, and peers can foster a more understanding atmosphere, allowing those with ADHD to thrive academically and socially. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by individuals with ADHD, we can work towards more inclusive practices that support their needs and promote their strengths.
An Introduction to the Pomodoro Technique
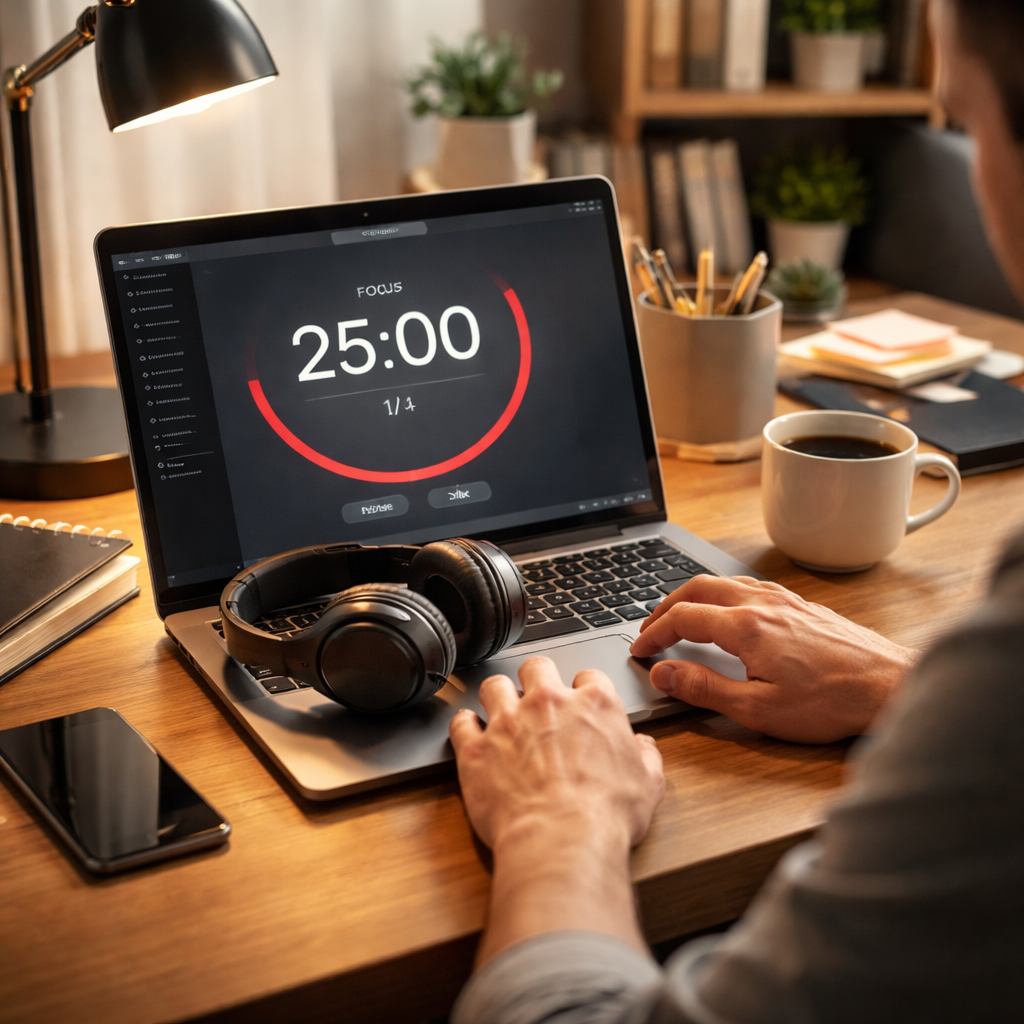
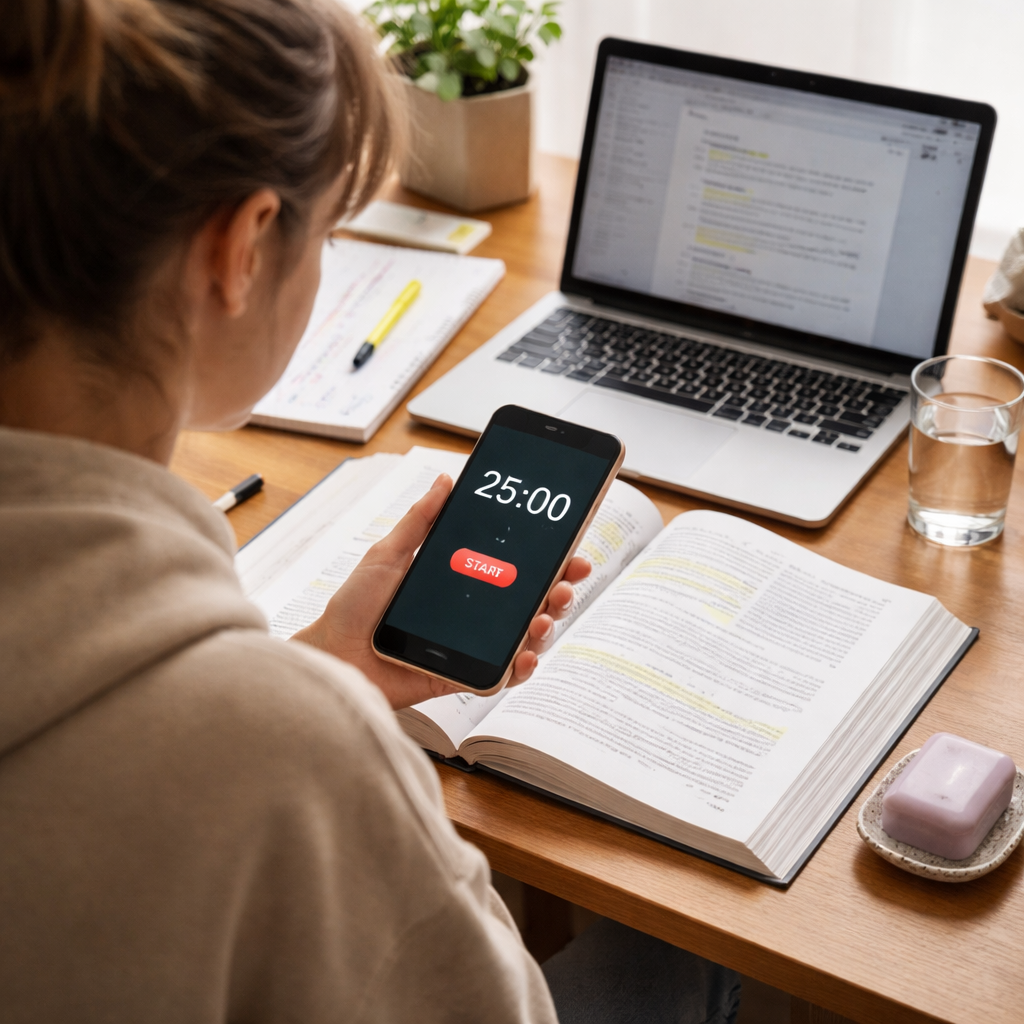
The Pomodoro Technique, developed by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s, is based on the idea of breaking work into manageable intervals. Each interval, known as a “Pomodoro,” is traditionally 25 minutes long, followed by a 5-minute break. After completing four Pomodoros, users take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The Origin of the Pomodoro Technique
The origin of the term “Pomodoro” comes from the Italian word for tomato, inspired by the timer Cirillo used, which resembled a tomato. The approach aims to enhance efficiency and focus by creating a structured work rhythm, making it easier for individuals, especially those with ADHD, to tackle challenging tasks in a less overwhelming manner. This technique not only helps in managing time but also encourages a sense of accomplishment as each Pomodoro completed is a step toward the larger goal.
The Basic Principles of the Pomodoro Technique
At its core, the Pomodoro Technique is about time management through intervals. The key steps include:
- Choose a task you want to work on.
- Set a timer for 25 minutes.
- Work on the task until the timer rings.
- Take a 5-minute break.
- Repeat this process and take a longer break after completing four intervals.
These principles promote sustained concentration while providing scheduled breaks, which can significantly help ADHD students manage their focus throughout their studies. The breaks are essential as they allow the brain to rest and recharge, reducing mental fatigue and enhancing overall productivity. During these short breaks, individuals can engage in activities that help them relax, such as stretching, walking, or even practicing mindfulness, which can further improve their focus for the next Pomodoro.
Moreover, the Pomodoro Technique encourages reflection and adaptation. After completing a series of Pomodoros, users are often advised to review their productivity and assess what worked well and what didn’t. This reflective practice not only fosters a deeper understanding of personal work habits but also allows for the fine-tuning of strategies to enhance efficiency in future tasks. By keeping track of completed Pomodoros, individuals can gain insights into their work patterns, helping them to set realistic goals and manage their time more effectively in the long run.
The Science Behind the Pomodoro Technique
Several studies support the idea that structured time management techniques can benefit individuals with focus-related difficulties. The Pomodoro Technique not only addresses concentration but also fosters goal-setting and time awareness. By breaking work into manageable intervals, typically 25 minutes long, followed by a short break, this method encourages a rhythm that can be particularly helpful for those who find it challenging to maintain attention over extended periods. This structured approach can transform daunting tasks into achievable segments, making it easier to start and sustain momentum.
The Role of Time Management in Concentration
Effective time management is crucial for enhancing concentration levels. Research shows that individuals perform better when they can allocate their time in defined chunks, helping to minimize distractions and procrastination. This is particularly relevant for ADHD students, who may struggle with perception of time and task completion. By implementing techniques like the Pomodoro, students can develop a clearer understanding of how long tasks take, which can lead to improved self-regulation and a sense of accomplishment. Furthermore, the predictability of the Pomodoro intervals can create a structured environment that reduces anxiety, allowing students to focus more on the task at hand rather than the overwhelming nature of their workload.
How Breaks Enhance Focus and Productivity
Regular breaks are essential for maintaining cognitive function. Studies indicate that short breaks can significantly enhance brain performance by allowing for mental recovery and reducing fatigue. For ADHD students, these breaks are particularly vital; they can step away from the task, recharge, and return with renewed focus. Additionally, during these breaks, engaging in physical activity or mindfulness exercises can further boost cognitive performance. Research suggests that even a brief walk or stretching can increase blood flow to the brain, enhancing overall mental clarity and creativity. This holistic approach to breaks not only aids in sustaining attention but also promotes a healthier lifestyle, which is beneficial for long-term productivity and well-being.
Applying the Pomodoro Technique to ADHD Students
Implementing the Pomodoro Technique for ADHD students requires thoughtful adaptation to cater to their needs. This customization can maximize the benefits of the technique and encourage positive studying habits. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by ADHD students, educators can create a more supportive learning environment that fosters concentration and productivity.

Tailoring the Pomodoro Technique for ADHD Students
For ADHD students, modifications may include adjusting the length of the Pomodoros or breaks. Some individuals may find that 15 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break is more effective. Others may prefer to use visual timers or integrate physical movement during breaks to enhance their overall engagement with the process. Finding the right balance is key to effectiveness. Additionally, incorporating sensory tools such as fidget spinners or stress balls during study sessions can help maintain focus and reduce anxiety, allowing students to channel their energy constructively while adhering to the structured intervals of the Pomodoro Technique.
Overcoming Potential Challenges in Implementation
While the Pomodoro Technique can be beneficial, challenges can arise, such as resistance to timed constraints or difficulty returning to work after breaks. To combat these issues, educators and caregivers can help motivate students by emphasizing the benefits of clear structure and by actively involving them in the creation of their Pomodoro schedules. It may also be helpful to establish a reward system that acknowledges their efforts and progress, reinforcing positive behavior and encouraging persistence. Furthermore, discussing the importance of self-regulation and time management skills can empower ADHD students, making them more invested in their learning process and more likely to embrace the Pomodoro Technique as a valuable tool in their academic journey.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the Pomodoro Technique for ADHD Students
As with any educational strategy, it is crucial to evaluate its effectiveness in practice. ADHD students can experience significant changes in their concentration levels, productivity, and overall academic performance when the Pomodoro Technique is appropriately implemented.
Short-Term and Long-Term Benefits
In the short term, students may notice improved focus and task completion rates. Long term, consistent application of the technique can foster better study habits, enhanced time management skills, and increased confidence in academic abilities.
Potential Limitations and Areas for Further Research
Despite its benefits, the Pomodoro Technique may not work for every student with ADHD. Individual differences in attention span and personal work styles may limit its effectiveness. Further research is needed to explore various adaptations and combinations of the Pomodoro Technique with other concentration-boosting strategies for ADHD students.
In conclusion, the Pomodoro Technique presents a structured yet flexible approach to enhance concentration in ADHD students. By providing manageable work intervals and encouraging regular breaks, it aligns well with the unique needs of these learners, paving the way for more effective study strategies and improved academic success.





